AES: Advanced Encryption Standard
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is one of the most important and widely used encryption algorithms in the digital world. This standard serves as a reliable method for protecting data against unauthorized access and is employed in numerous applications and security protocols. In this article, we will explore the details of AES, how it works, its features, and its applications.
- History of AES
DES (Data Encryption Standard) was widely used in the 1990s. However, this algorithm only provided 56-bit encryption, which could be broken within minutes using modern computers. There was a need for a stronger encryption method to thwart opportunistic data thieves. Eventually, AES was developed by two Belgian researchers. Government organizations like the NSA and major companies like Microsoft adopted this new encryption method by 2005, and it soon became a common standard for use in firewalls and VPNs.
- Structure of AES
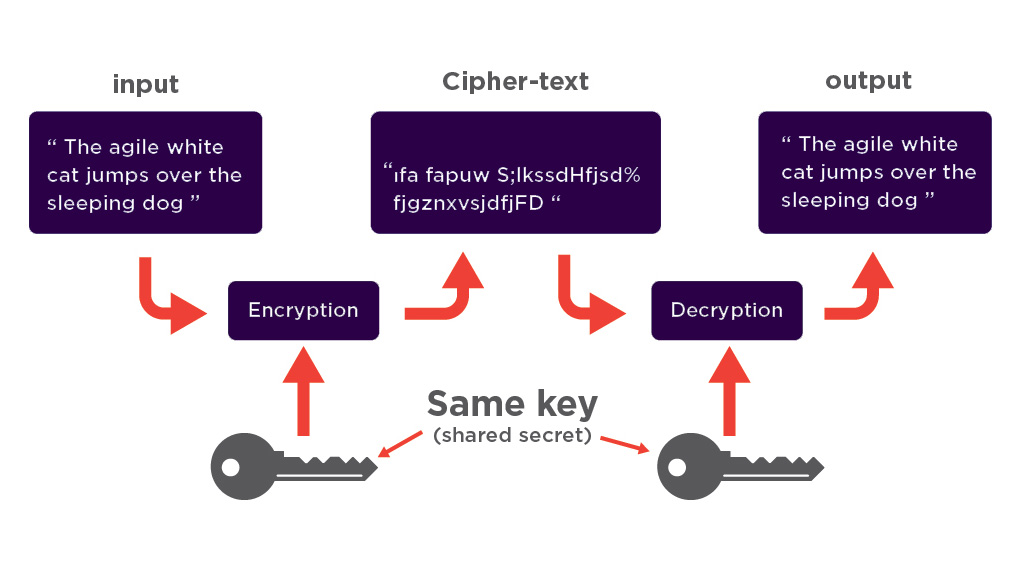
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a symmetric encryption algorithm used for encrypting and decrypting data. Simply put, this algorithm transforms data into pieces that are unreadable without access to the appropriate key. AES utilizes a symmetric block cipher algorithm to substitute, permute, and mix the data, making it more difficult to penetrate. This algorithm operates on 128-bit blocks and can use keys of 128, 192, and 256 bits.
- Types of AES Encryption
AES Encryption with 128-bit Key
In AES-128, the key length is 128 bits, which is why it is named as such. Without using an encryption key, the encrypted data is completely unintelligible. Is AES with a 128-bit key secure? Yes, because data undergoes ten rounds of encryption during the data compression process. Data pieces are taken and mixed according to a specified instruction based on the type of encryption. At this stage, a key is generated that allows anyone receiving the data to unlock the encryption network. Symmetric key algorithms (including AES-128) use the same key for both encrypting and decrypting messages. This makes them faster than asymmetric encryptions; hence, they are very suitable for encrypting VPN data.
AES Encryption with 256-bit Key
AES-256 was introduced as an alternative to AES-128 and is indeed a much more secure version of its predecessor. This algorithm uses 14 rounds of encryption instead of the 10 rounds used in AES-128, making it significantly more difficult for hackers to decrypt information. Is AES with a 256-bit key secure? This algorithm is used by the U.S. government to protect sensitive data, and it can be said that AES-256 is one of the most secure methods for ensuring data security (within reasonable limits). Although its speed is not as high as AES-128, AES-256 is certainly a more secure encryption option.
- Features and Advantages of AES
High Security: AES is one of the most secure encryption algorithms available, and no successful attacks against it have been reported.
Fast Performance: Compared to other symmetric encryption algorithms, AES has significantly faster performance.
Flexibility: With the ability to use different keys, AES can be tailored to meet various security needs.
Wide Support: Many security protocols like SSL/TLS and VPN use AES as their encryption standard.
- Applications of AES
Data Protection: In storing sensitive information such as financial, medical, and personal data.
Secure Communications: In communication protocols like HTTPS, VPN, and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA).
File Encryption: In file management software and security tools.
- Conclusion
As a global standard for data encryption, AES plays a crucial role in ensuring information security in the digital world. Given its high security and performance speed, this algorithm has become one of the main pillars of modern security systems. In today’s world, where cyber threats are increasingly on the rise, using AES as an effective solution for protecting information is essential.